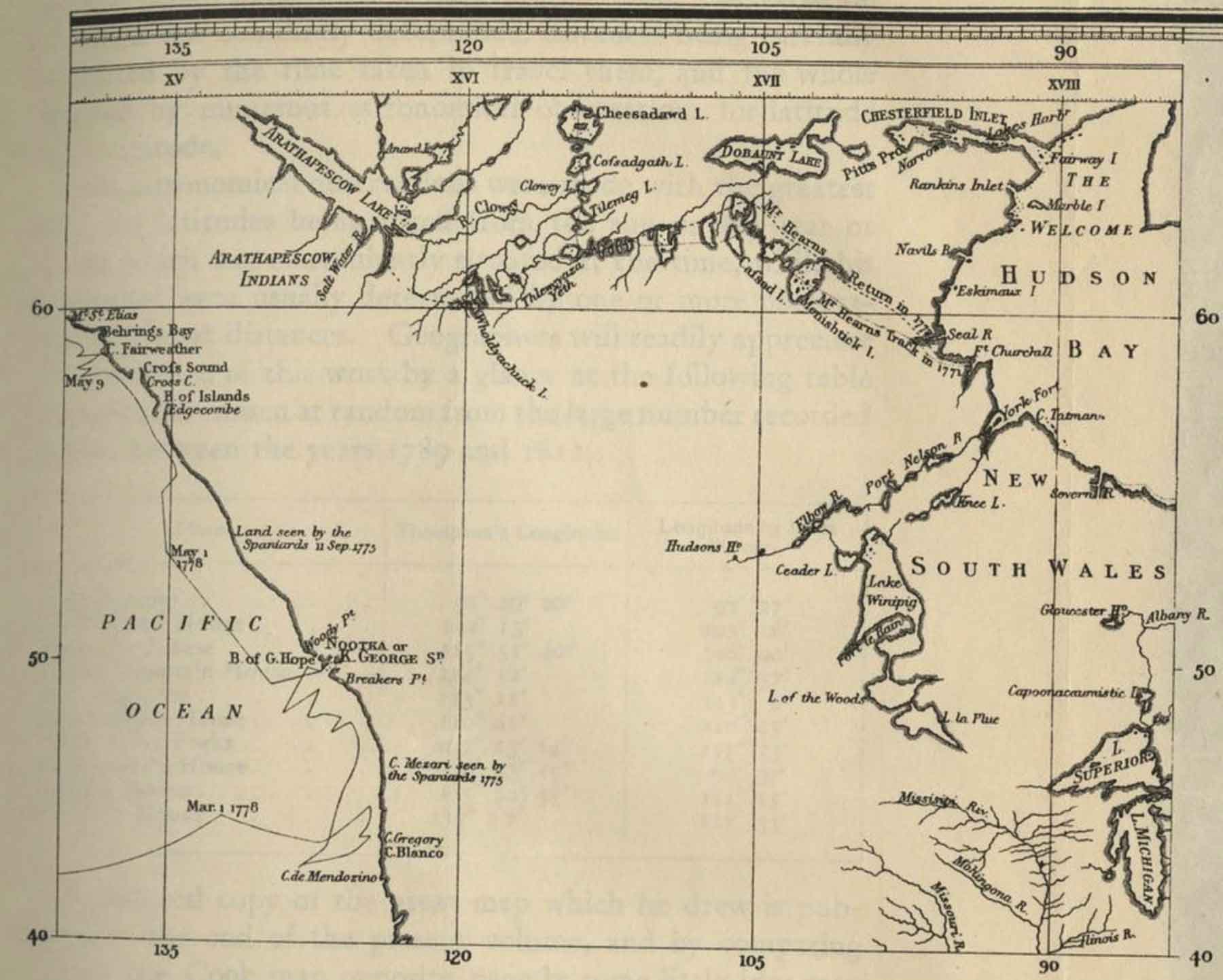
The lake appears as “Arathapescow Lake” on the chart accompanying
James Cook’s
A Voyage to the Pacific Ocean, published in 1784. The chart displays the voyages of Captain Cook; the details about the interior of North America came from fur trade sources.
Alexander Mackenzie [1764–1820], starting his voyage from Fort Chepewyan on Lake Athabasca to the Pacific Ocean in October 1792, wrote:
We entered the Peace River at seven in the morning of the 12th, taking a Westerly course. It is evident, that all the land between it and the Lake of the Hills, as far as the Elk River, is formed by the quantity of earth and mud, which is carried down by the streams of those two great rivers. In this space there are several lakes. The lake, Clear Water, which is the deepest, Lake Vassieu, and the Athabasca Lake, which is the largest of the three, and whose denomination in the Knistineaux language, implies, a flat low, swampy country, subject to inundations.
On the Mackenzie’s 1803 map, the lake appears as “Lake of the Hills.” On Aaron Arrowsmith’s 1795 map the lake is called “Athapescow Lake.”
The word Athabaskan is an anglicized version of a Cree language name for Lake Athabasca (Cree: Āðapāskāw “[where] there are reeds one after another”). Cree is one of the Algonquian languages and therefore not itself an Athabaskan language.
In the 18th century the territory around the lake was occupied by indigenous Dane-zaa (historically referred to as the Beaver tribe by Europeans) and Chipewyan people. Both are of the Athabaskan language family.
In Albert Lacombe’s Dictionnaire de la langue des Cris (1874), the lake and river are called “Athabaskaw” in the accompanying map, but there is not an entry for that specific word. Lacombe does cite as an unspecified place name “Ayabaskaw” or “Arabaskaw,” meaning “il y a des joncs ou du foin ça et là” [There are rushes and hay here and there] (p. 705).
In 1790, it was referred to as “Lake of the Hills,” and the river, the Great Arabuska. Lake of the Hills may have been a more genteel translation of the name for the lake at the time. Peter Fidler recorded the Cree name as Too-toos Sack-a-ha-gan, and the Chipewyan name as Thew Too-ak. The literal translation of the Cree name is “breast” lake, referring to the north-west shore, which according to Philip Turnor in 1791, came “from their appearing high and rounded at a distance.”
However, the most commonly accepted version of the origin of the name is from the Cree, where it is said to mean “where there are reeds,” referring to the muddy delta of the river where it falls into Lake Athabasca. Of this portion of it, Turner wrote “low swampy ground on the South side with a few willows growing upon it, from which the Lake in general takes its name Athapison in the Southern [Cree] tongue [which] signifies open country such as lakes with willows and grass growing about them.” In 1820, George Simpson of the Hudson’s Bay Company referred to it as the “Athabasca or Elk River.”
“Athabasca, Lake / Lac Athabasca” is among the 75 “Pan-Canadian names,” large and well-known Canadian features and areas designated in Treasury Board Circular 1983-58 to require presentation in both official languages of Canada on federal maps.